Clin Exp Allergy: H3K27me3去甲基化酶抑制哮喘
發(fā)布日期:2018-11-26
原標(biāo)題:H3K27me3去甲基化酶逆轉(zhuǎn)氣道平滑肌表型抑制哮喘
延伸閱讀

Clinical & Experimental Allergy
DOI: 10.1111/cea.13244
Abstract:
Background: The shift in airway smooth muscle cells (ASMCs) phenotype between proliferation and contraction during asthma has been reported recently, highlighting a role of ASMCs plasticity in the pathophysiology of asthma. As an event involved in epigenetic post-translational modification, histone H3 lysine27 (H3K27) demethylation has attracted significant attention with respect to the epigenetic changes in diverse cells; however, little is known about its contribution to the switching of ASMCs phenotype in asthma .
Methods: Mice were exposed five times a week to house dust mite (HDM) extract for 5 weeks. Lung function was measured following the final HDM challenge. Airway inflammation and remodelling were then assessed in lungs of individual mice. Human ASMCs were purchased from Sciencell Research Laboratories. Proliferation, synthesis,migration and contraction of ASMCs were analyzed, respectively.
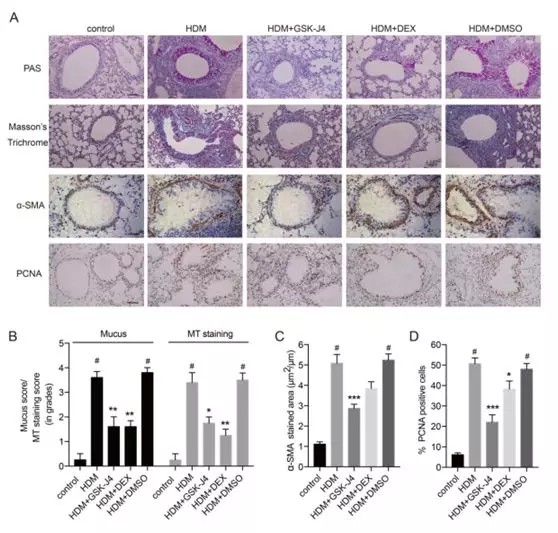
Results: We observed demethylation at H3k27me3 sites in lungs harvested from mice exposed to house dust mite (HDM) extract. Administration of a selective inhibitor of H3K27 demethylase (GSK-J4) could ameliorate the classical hallmarks of asthma, such as airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR), airway inflammation and remodelling. We established a proliferative as well as a contractive model of human ASMCs to explore the impacts of H3K27 demethylase inhibition on ASMCs phenotype. Our results indicated that GSK-J4 decreased ASMCs proliferation and migration elicited by PDGF through the Akt/JNK signalling; GSK-J4 also prevented the upregulation of contractile proteins in ASMCs induced by TGF-β through the Smad3 pathway .
Conclusions: Inhibition of H3K27me3 demethylation alleviated the development of asthmatic airway disease in vivo and modulated ASMCs phenotype in vitro. Collectively, our findings highlight a role of H3K27me3 demethylation in experimental asthma and ASMCs phenotype switch .
First Author:
Qijun Yu
Correspondence:
Department of Respiratory & Critical Care Medicine
All Authors:
Qijun Yu, Xiaowei Yu, Wenxue Zhao, Manni Zhu, Zhengxia Wang, Jiaxiang Zhang,Mao Huang, Xiaoning Zeng


——來(lái)自浙大迪迅
?、?最近研究表明哮喘時(shí)氣道平滑肌細(xì)胞(ASMC)表型在增生和收縮之間的變化,強(qiáng)調(diào)了ASMC的可塑性在哮喘病理生理學(xué)中的作用;② 小鼠每周在屋塵螨提取物中暴露5次,共試驗(yàn)5周;③ 給予H3K27去甲基化酶抑制劑(GSK-J4)可改善哮喘的經(jīng)典特征,如氣道高反應(yīng)性(AHR)、氣道炎癥和重塑;④ GSK-J4通過(guò)Akt/JNK信號(hào)轉(zhuǎn)導(dǎo)途徑抑制PDGF誘導(dǎo)的ASMCs增殖和遷移;GSK-J4還通過(guò)Smad3途徑抑制TGF-β誘導(dǎo)的ASMCs收縮蛋白的上調(diào);⑤ 抑制H3K27me3去甲基化可減輕哮喘氣道疾病的發(fā)生,體外調(diào)節(jié)ASMCs表型。
延伸閱讀

Clinical & Experimental Allergy
[IF:5.158]
Inhibition of H3K27me3 demethylases attenuates asthma by reversing the shift in airway smooth muscle phenotypeDOI: 10.1111/cea.13244
Abstract:
Background: The shift in airway smooth muscle cells (ASMCs) phenotype between proliferation and contraction during asthma has been reported recently, highlighting a role of ASMCs plasticity in the pathophysiology of asthma. As an event involved in epigenetic post-translational modification, histone H3 lysine27 (H3K27) demethylation has attracted significant attention with respect to the epigenetic changes in diverse cells; however, little is known about its contribution to the switching of ASMCs phenotype in asthma .
Methods: Mice were exposed five times a week to house dust mite (HDM) extract for 5 weeks. Lung function was measured following the final HDM challenge. Airway inflammation and remodelling were then assessed in lungs of individual mice. Human ASMCs were purchased from Sciencell Research Laboratories. Proliferation, synthesis,migration and contraction of ASMCs were analyzed, respectively.
Results: We observed demethylation at H3k27me3 sites in lungs harvested from mice exposed to house dust mite (HDM) extract. Administration of a selective inhibitor of H3K27 demethylase (GSK-J4) could ameliorate the classical hallmarks of asthma, such as airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR), airway inflammation and remodelling. We established a proliferative as well as a contractive model of human ASMCs to explore the impacts of H3K27 demethylase inhibition on ASMCs phenotype. Our results indicated that GSK-J4 decreased ASMCs proliferation and migration elicited by PDGF through the Akt/JNK signalling; GSK-J4 also prevented the upregulation of contractile proteins in ASMCs induced by TGF-β through the Smad3 pathway .
Conclusions: Inhibition of H3K27me3 demethylation alleviated the development of asthmatic airway disease in vivo and modulated ASMCs phenotype in vitro. Collectively, our findings highlight a role of H3K27me3 demethylation in experimental asthma and ASMCs phenotype switch .
First Author:
Qijun Yu
Correspondence:
Department of Respiratory & Critical Care Medicine
All Authors:
Qijun Yu, Xiaowei Yu, Wenxue Zhao, Manni Zhu, Zhengxia Wang, Jiaxiang Zhang,Mao Huang, Xiaoning Zeng
2018-11-13 Article
創(chuàng)建過(guò)敏性疾病的科研、科普知識(shí)交流平臺(tái),為過(guò)敏患者提供專業(yè)診斷、治療、預(yù)防的共享平臺(tái)。

 杭州浙大迪迅生物基因工程有限公司
杭州浙大迪迅生物基因工程有限公司

