Release date:2020-06-05
Allergy
[IF:6.048]
Colony‐stimulating factor 1 and its receptor are new potential therapeutic targets for allergic asthma DOI: 10.1111/all.14011
Abstract:
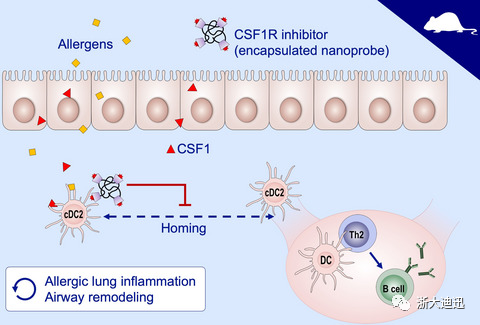
Background: A new approach targeting aeroallergen sensing in the early events of mucosal immunity could have greater benefit. The CSF1‐CSF1R pathway has a critical role in trafficking allergens to regional lymph nodes through activating dendritic cells. Intervention in this pathway could prevent allergen sensitization and subsequent Th2 allergic inflammation.
Methods: We adopted a model of chronic asthma induced by a panel of three naturally occurring allergens and novel delivery system of CSF1R inhibitor encapsulated nanoprobe.
Results: Selective depletion of CSF1 in airway epithelial cells abolished the production of allergen‐reactive IgE, resulting in prevention of new asthma development as well as reversal of established allergic lung inflammation. CDPL‐GW nanoprobe containing GW2580, a selective CSF1R inhibitor, showed favorable pharmacokinetics for inhalational treatment and intranasal insufflation delivery of CDPL‐GW nanoprobe ameliorated asthma pathologies including allergen‐specific serum IgE production, allergic lung and airway inflammation and airway hyper‐responsiveness (AHR) with minimal pulmonary adverse reaction.
Conclusion: The inhibition of the CSF1‐CSF1R signaling pathway effectively suppresses sensitization to aeroallergens and consequent allergic lung inflammation in a murine model of chronic asthma. CSF1R inhibition is a promising new target for the treatment of allergic asthma.
First Author:
Hyung‐Geun Moon
Correspondence:
Hyung‐Geun Moon and Gye Young Park,Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, Sleep and Allergy, University of Illinois at Chicago,840 S. Wood St. CSB‐920N, Chicago, IL 60612, USA.
All Authors:
Hyung‐Geun Moon, Seung‐jae Kim, Myoung Kyu Lee, Homan Kang, Hak Soo Choi, Anantha Harijith, Jinhong Ren, Viswanathan Natarajan, John W. Christman, Steven J. Ackerman, Gye Young Park
2020-06-15 Article
 杭州浙大迪迅生物基因工程有限公司
杭州浙大迪迅生物基因工程有限公司
