Release date:2020-04-30
Molecular Immunology Volume 70, February 2016,Pages 125-133
[IF:3.188]
Using patient serum to epitope map soybean glycinins reveals common epitopes shared with many legumes and tree nutshttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2015.12.008
Abstract:
Highlights ?
The IgE-binding B-cell epitopes of two similar soybean glycinin subunits (Gly m 6) are described.
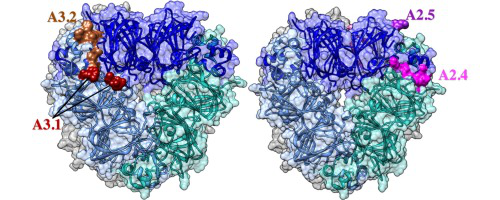
? Three-dimensional modeling of the glycinin hexamers located most epitopes on the exposed surfaces.
? Comparison with other plant 11S storage protein sequences revealed one dominant and several shared epitopes.
? Common epitope hot spots are often shared between plant storage proteins from diverse families.
Abstract
Soybean consumption is increasing in many Western diets; however, recent reviews suggest that the prevalence of soy allergy can be as high as 0.5% for the general population and up to 13% for children. The immunoglobulin-E (IgE) binding of sera from six soy-sensitive adult human subjects to soybean proteins separated by 2D gel electrophoresis was studied.
Synthetic peptide sets spanning the mature glycinin subunit A2 and A3 primary sequences were used to map the IgE-binding regions. Putative epitopes identified in this study were also localized on glycinin hexamer models using bioinformatics software.
We identified linear IgE-binding epitopes of the major storage protein Gly m 6 by screening individual soy-sensitive patient sera. These epitopes were then further analysed by 3D in silico model localization and compared to other plant storage protein epitopes. Web-based software applications were also used to study the ability to accurately predict epitopes with mixed results. A total of nine putative IgE-binding epitopes were identified in the glycinin A3 (A3.1–A3.3) and A2 (A2.1–A2.6) subunits.
Most patients' sera IgE bound to only one or two epitopes, except for one patient's serum which bound to four different A2 epitopes. Two epitopes (A3.2 and A2.4) overlapped with a previously identified epitope hot spot of 11S globulins from other plant species. Most epitopes were predicted to be exposed on the surface of the 3D model of the glycinin hexamer. Amino acid sequence alignments of soybean acidic glycinins and other plant globulins revealed one dominant epitope hot spot among the four reported hot spots. This study may be helpful for future development of soy allergy immunotherapy and diagnosis.
All Authors:
Hanaa Saeed Christine Gagnon Elroy Cober Steve Gleddie
2020-1-17 Article
 杭州浙大迪迅生物基因工程有限公司
杭州浙大迪迅生物基因工程有限公司
